forum
library
tutorial
contact

Replacing Megawatts
by Linwood LaughyMoscow-Pullman Daily News, March 3, 2023
|
the film forum library tutorial contact |

|
Replacing Megawattsby Linwood LaughyMoscow-Pullman Daily News, March 3, 2023 |
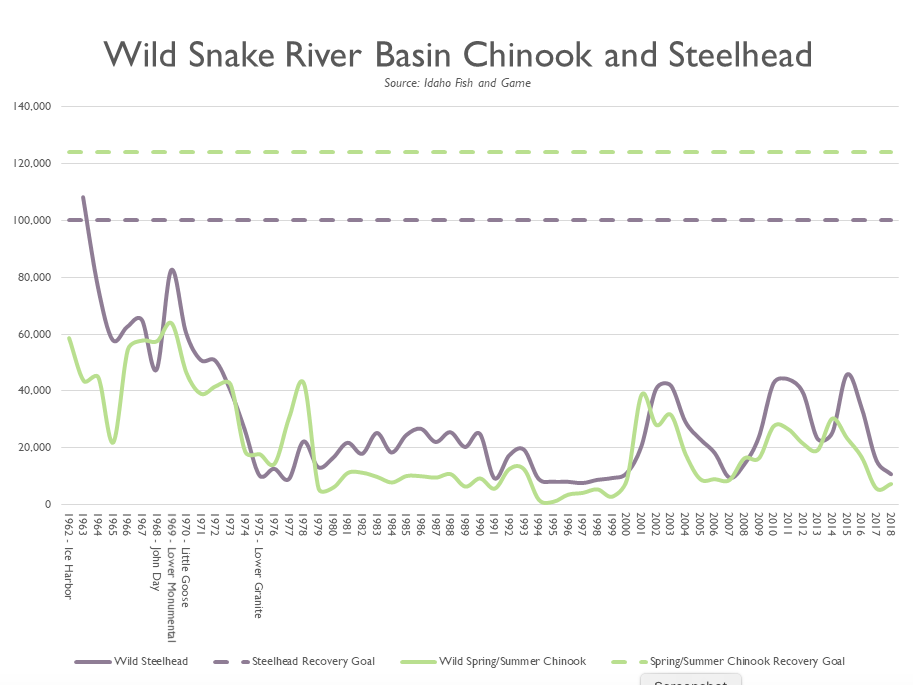 The four Lower Snake River dams combined have a power-generation capacity of 3,030 average megawatts, but annually produce on average only about 925 average megawatts due largely to a lack of water. According to the Inslee-Murray "Benefit Replacement Report," power generated by the Lower Snake River dams must be replaced before these dams can be breached.
The four Lower Snake River dams combined have a power-generation capacity of 3,030 average megawatts, but annually produce on average only about 925 average megawatts due largely to a lack of water. According to the Inslee-Murray "Benefit Replacement Report," power generated by the Lower Snake River dams must be replaced before these dams can be breached.
In its "2021 Power Plan," the Northwest Power and Conservation Council reported that between 2018 and 2028, coal-fired power generation capacity serving the Pacific Northwest would decline from 7,000 average megawatts to 2,400. Four coal-fired plants were shuttered in 2020 alone. The council's projected loss of 4,600 average megawatts represents the equivalent capacity of six Lower Snake River dams.
No governor or U.S. senator claimed this disappearing power must be replaced before the coal plants could be closed.
When energy suppliers identify a future need for additional power, they often post a "request for proposals." In 2020, for example, PacificCorp requested bids for 4,300 average megawatts of renewable energy resources available by 2024. Bidders responded with proposed projects totaling 36,000 average megawatts -- eight times the requested supply.
Bonneville Power Administration markets the power from 31 federal dams, most in the Columbia River Basin. If Bonneville posted a request for proposals for renewable energy equivalent to the power capacity of the Lower Snake River dams, the requirement for "replacement before breaching" would soon disappear. The Lower Snake River dams could then be breached, and wild Snake River salmon and steelhead begin their path to recovery.
learn more on topics covered in the film
see the video
read the script
learn the songs
discussion forum
