"We are evaluating the costs, benefits and tradeoffs, including how the alternatives affect
congressionally authorized purposes of the federal projects, and resources such as fish and wildlife,"
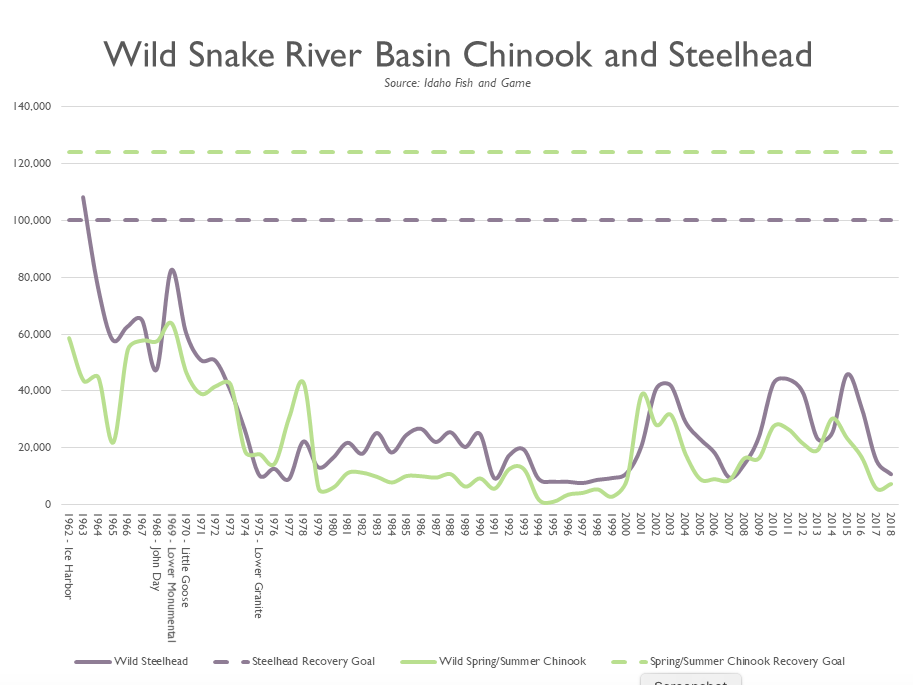 The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers released an update May 17 which provides many new details about the five alternatives in the upcoming draft environmental impact statement (EIS) for operating 14 dams on the Snake and Columbia rivers.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers released an update May 17 which provides many new details about the five alternatives in the upcoming draft environmental impact statement (EIS) for operating 14 dams on the Snake and Columbia rivers.
Scheduled for release in February 2020, the draft EIS is expected to include a "reasonable range of alternatives" being considered for long-term operations, maintenance and configuration of the major Corps and Bureau of Reclamation dams in the Columbia Basin.
The update includes a 20-minute webcast explaining the process of evaluating potential social and environmental impacts analyzed in five alternatives, each designed to meet multiple objectives.
The alternatives include:
- a "no action" or status quo option;
- a flexible spill operation;
- a low carbon priority option;
- an alternative that would breach the four lower Snake River dams;
- and an option for spilling up to 125 percent total dissolved gas (TDG) at the eight lower Snake and Columbia river dams.
"For each of the five alternatives, we are evaluating the costs, benefits and tradeoffs, including how the alternatives affect congressionally authorized purposes of the federal projects, and resources such as fish and wildlife," the webcast says. "We may select the preferred alternative from any of the alternatives that we are analyzing. We may also make minor adjustments to an existing alternative, within the flexibility allowed under NEPA [National Environmental Policy Act], by adding or removing measures analyzed within the EIS to identify the preferred alternative," it says.
Each alternative seeks to comply with environmental laws while retaining the multiple purposes of the federal projects. Those purposes include flood risk management, power production, fish and wildlife protection, navigation, irrigation, recreation, and municipal and industrial water supply.
According to the webcast, several measures will be included in most or all of the alternatives, except for the no action alternative, including these:
- Flood risk management would be updated at Libby and Grand Coulee dams to provide more flexibility for better flood storage, and to augment water releases and habitat for fish. At Libby Dam, local forecast conditions would partly dictate operations, and at Grand Coulee Dam, the draft rate would be reduced in April by releasing more water earlier in wetter years to reduce the risk of shoreline erosion.
- Water supply for authorized irrigation would include additional pumping from reservoirs behind Grand Coulee and Hungry Horse dams, and for the Chief Joseph Dam project.
- Fish passage would be improved at some dams through surface passage structures, upgraded spillway weirs, lamprey passage structures and improved fish ladders. At Lower Monumental and Ice Harbor dams, a pumping system would provide cooler water for fish ladders to encourage adults to continue migrating upstream. Water releases in the summer would be modified based on local streamflow forecasts.
- Power generation would be "slightly" more flexible by allowing more water to collect in the forebay during fish passage season. This would allow renewables such as wind and solar energy to be better integrated, as more hydropower would be available when renewables are not.
The webcast also offers a "deep dive" into the differences between the alternatives.
- Alternative 1 uses an
- alternating spill pattern for juvenile fish passage in the spring, and provides more spill than the no action alternative. It would spill up to 115 percent TDG in the forebays and 120 percent TDG in the tailraces at dams, alternating with a base spill to performance standards. In the summer months, spill could end earlier in August at Snake River projects when benefits to fish are limited because few fish migrate downstream. The end date would be triggered by juvenile fish counts.
- Fish transport would begin 10 days earlier, on April 15.
- Cool water from Dworshak Dam would be released earlier and later--from June through September, but reduced in August--to help migrating adult salmon and steelhead over a longer period.
- Alternative 2 adds measures to prioritize a low carbon power system.
- It provides the least amount of spill, reduced to near 110 percent TDG.
- It would curtail spill and send more water through the powerhouses in August, when the region's demand for power is greatest.
- The 110 percent TDG would increase power generation through the spring and summer.
- Spill at some projects might be higher to meet minimum requirements for safe operations and specific issues at certain dams.
- This alternative also removes restrictions to operate run-of-river projects at minimum operating pool and minimum irrigation pool to provide more flexibility to shape flows within the day or between days.
- Run-of-river projects would also have no restrictions on turbine operating range to help integrate renewables and help manage TDG levels during high flows.
- Storage projects would be drafted slightly deeper in the winter and early spring. This would allow for more generation during winter's high demand.
- It also increases the duration when Snake River dams can operate at zero generation outside the fish passage season, enabling those dams to hold water for a few hours during the day for later use when wind or solar are not available.
- Fish transport would increase due to less spill, and would run from April 25 to Aug. 31.
- Fish screens would be removed except at projects where fish are collected for transport. That would increase generation efficiency and make conditions less turbulent for fish, although more fish would pass through turbines.
- Alternative 3 calls for breaching the four lower Snake River dams. The Corps' webcast notes that breaching is different from removing a dam, which is far costlier because it would take out the concrete powerhouses, navigation locks and other structures.
- Instead, earthen embankments at Lower Granite, Little Goose, Lower Monumental and Ice Harbor dams would be removed while the actual dams would remain in place but would not operate.
- The dams would then spill to 120 percent TDG for 24 hours a day in the spring at the eight lower Snake and Columbia river dams to mid-June.
- Dams would then go to summer spill at the same level as the no action alternative through July 31.
- Minimum irrigation and minimum pool restrictions at John Day Dam would be removed,
- and Libby Dam might draft deeper at the end of December.
- To help integrate renewables, the lower Columbia River dams would have fewer restrictions on turbine operating range and get more flexibility for power generation.
- Alternative 4 features
- spilling to 125 percent TDG at the eight lower Snake and Columbia river dams from March 1 to Aug. 31.
- This alternative includes spill for steelhead in March, October and November,
- and drawdowns in storage projects to provide enough water.
- Instead of upgrading spillway weirs, this option would add notched gate inserts to spillway weirs to provide surface passage for adult fish at lower flows and allow for smaller spill levels than unmodified weirs for spilling in October and November.
- In drier years, Grand Coulee and other upstream reservoirs would augment flows by up to 2 million acre feet to meet downstream flow targets at McNary Dam designed to benefit ESA-listed fish.
- The eight lower Snake and Columbia river projects would see drawdowns in the spring and summer, mostly to minimum operating pools.
- Juvenile fish would be transported from April 25 to June 15, and from Aug. 15 to Nov. 15.
- Discharges would be limited from Libby Dam in the winter to help establish vegetation for resident fish.
- The no action alternative would continue operations according to rules in effect in September 2016, when the co-lead agencies--the Corps, the Bureau of Reclamation and the Bonneville Power Administration--filed a notice of intent to prepare the EIS. It includes the actions that were proposed in the previous Endangered Species Act consultations with NOAA Fisheries and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, such as the improved fish passage turbines planned for Ice Harbor and McNary dams, and would follow the 2016 Fish Operations Plan.
The Corps also updated its Columbia River System Operations website with stories on the no action alternative, the NEPA process and other informational articles.
K.C. Mehaffey
EIS Alternatives Range From Low Carbon to 125 Percent TDG Spill
NW Fishletter, June 3, 2019
See what you can learn
learn more on topics covered in the film
see the video
read the script
learn the songs
discussion forum



 The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers released an update May 17 which provides many new details about the five alternatives in the upcoming draft environmental impact statement (EIS) for operating 14 dams on the Snake and Columbia rivers.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers released an update May 17 which provides many new details about the five alternatives in the upcoming draft environmental impact statement (EIS) for operating 14 dams on the Snake and Columbia rivers.
